Introduction
This article is aimed at operation managers at any level who want to take advantage of the new technologies of AR, VR, and MR. We will briefly discuss these technologies, describe some trends and general usage, and emphasize their significant benefits for operations managers.
Section 1: Understanding AR, VR, and MR
Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) are transformative technologies reshaping the way we interact with the digital and physical worlds.
- AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing our perception with data, and making it invaluable for tasks like navigation and maintenance.
- VR immerses users in entirely digital environments, revolutionizing training, gaming, and simulations.
- MR bridges the gap by integrating digital elements into the physical world, enabling seamless interactions with both.
Collectively, these technologies empower industries from healthcare to manufacturing, unlocking new dimensions of efficiency, collaboration, and innovation, and are poised to play an even greater role in our interconnected future.
The usage of these technologies is growing very rapidly, as can be seen from the below chart.
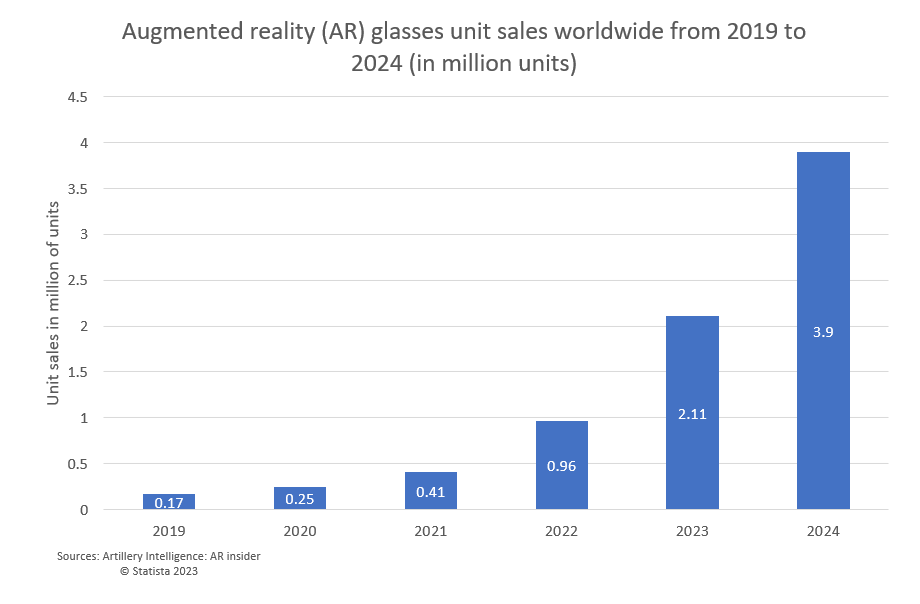
Selecting the proper hardware, but without great software, is totally useless.
Section 2: Improving Training and Onboarding
Training and onboarding have undergone a profound transformation with the integration of Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) technologies. These immersive tools have revolutionized the way employees are introduced to new roles and tasks.
- AR enhances onboarding by overlaying contextual information onto the real-world environment, providing step-by-step guidance, real-time data, and active remote collaboration. New employees can quickly adapt to their roles, reducing the learning curve.
- VR offers a simulated environment for hands-on training, enabling employees to practice tasks and scenarios without real-world consequences. This is especially valuable in industries with complex devices like healthcare, printing, agro-mechanics, and aviation, where precision and safety are paramount.
- MR combines the best of both AR and VR, allowing trainees to interact with physical objects while benefiting from digital assistance. For example, an engineer can receive real-time guidance and data overlays while working on complex machinery.
These technologies also enable remote training, reducing the need for physical presence and ensuring consistency in training across geographical locations. In conclusion, AR, VR, and MR have streamlined training and onboarding, significantly improved retention rates and overall workforce productivity, and reduced safety cases while training.
Section 3: Enhancing Remote Collaboration
Remote collaboration in operations has become increasingly essential in our interconnected world, and Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) technologies play pivotal roles in enhancing this collaborative landscape.
- AR empowers remote teams by providing real-time visual guidance and data overlays, enabling experts to assist field workers from afar. For instance, a technician wearing AR glasses can receive step-by-step instructions while working on equipment, reducing downtime and travel costs.
- VR creates immersive virtual meeting spaces where team members from different locations can interact as if they were in the same room. This fosters a sense of presence and enables collaborative brainstorming, design reviews, and training sessions without needing physical presence.
- MR merges the physical and digital realms, allowing remote and on-site team members to share experiences and collaborate seamlessly. Architects, for example, can collaborate on construction projects by visualizing plans in real-world contexts.
These technologies break down geographical barriers, enhance real-time communication, and promote effective decision-making in operations, ultimately leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved outcomes for remote teams. As remote collaboration continues to evolve, AR, VR, and MR will remain instrumental in shaping the future of operations.
Section 4: Streamlining Operations
Virtual Reality (VR) offers remarkable potential in streamlining operations by simulating manufacturing processes and optimizing workflows. By creating realistic virtual environments, VR enables manufacturers to conduct detailed simulations of their production processes. This allows for testing and refining procedures without any impact on the actual production line. Workers can practice their tasks, identify bottlenecks, and fine-tune processes for maximum efficiency. As a result, VR reduces downtime, minimizes errors, and enhances overall productivity.
Mixed Reality (MR) is a game-changer on the factory floor by providing contextual information for decision-making. With MR headsets, workers can access real-time data, schematics, and instructions overlaid onto their physical surroundings. For instance, a technician repairing machinery can see diagnostic information, step-by-step repair guides, and safety alerts displayed in their field of vision. This hands-free access to critical information enhances decision-making, reduces the risk of errors, and accelerates troubleshooting and maintenance tasks. MR improves productivity and contributes to a safer and more informed workforce, ultimately streamlining operations and ensuring smoother production processes.
Section 5: Improving Maintenance and Repairs
Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR) are changing maintenance and repair operations in the mechanical industry, significantly enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime.
AR provides technicians with visual guidance and real-time data during maintenance and repairs. For instance, when servicing complex machinery, technicians can wear AR glasses that display schematics, checklists, and step-by-step guidance directly in their field of view. This minimizes the need to consult manuals, speeding up the repair process and reducing the risk of errors.
MR takes this a step further by integrating digital elements seamlessly into the physical environment. Technicians can collaborate with remote experts in real time, sharing a common view of the equipment and receiving guidance through holographic annotations and instructions. This remote assistance is invaluable for tackling complex issues that require specialized knowledge.
Section 6: Data Analytics
When utilizing AR, VR, and MR technologies, real-time monitoring is inherently integrated, offering crucial insights for planners and decision-makers. This data encompasses information on time durations, decisions executed by operators or technicians, occurrences of errors, as well as safety and near-safety incidents.
This invaluable dataset is gathered seamlessly, without disrupting regular operations, serving as a pivotal element in driving ongoing enhancements within operational processes.
Section 7: Cost Savings and ROI
The aforementioned factors collectively result in substantial cost reductions and a noteworthy return on investment (ROI) when leveraging AR, VR, and MR technologies. Numerous documented instances underscore these savings, and here are just two examples:
An article authored by Emily Friedman[1] highlights ten notable use cases that have yielded substantial cost savings.
Furthermore, a blog post published by Caroline Letrange[2] in March 2023 reports a remarkable 35% increase in efficiencies and a substantial 40% reduction in errors.
These data points unequivocally affirm that when approached thoughtfully—by selecting the right operations, appropriate hardware, and, most crucially, the software for seamless integration—embracing AR, VR, and MR technologies can generate an outstanding ROI.
All the above reasons lead to significant cost savings and high ROI using AR, VR, and MR technologies
Conclusion
In the fast-evolving landscape of technology, Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) stand as transformative tools for operations managers seeking to innovate, streamline processes, and optimize their teams’ performance.
Our journey through these immersive technologies has shown their remarkable potential. AR enriches onboarding with real-world context and active collaboration, while VR immerses employees in lifelike simulations, and MR elegantly combines physical and digital realms for enhanced learning and hands-on experience.
Moreover, these technologies are breaking geographical boundaries, fostering efficient remote collaboration, and empowering decision-makers with real-time insights. VR’s capacity to simulate manufacturing processes and MR’s contextual information delivery are revolutionizing operations, reducing downtime, and boosting productivity.
Mechanical operations benefit from AR’s visual guidance and MR’s remote assistance, reducing errors and downtime. Real-time monitoring across AR, VR, and MR seamlessly provides data crucial for optimizing operations.
Ultimately, the undeniable evidence of substantial cost savings and a promising return on investment underscores the importance of selecting the right technologies, hardware, and software for effective integration. AR, VR, and MR are more than tools; they are keys to unlocking the future of operational excellence.



